What does Browserbase actually do?
Browserbase began with a simple yet bold vision: the world needed a new kind of browser specifically designed for automated, AI-driven interactions. In his founding memo, CEO Paul Klein IV questioned why we were still building web infrastructure for humans when almost half of internet traffic is generated by bots. Combined with the explosion of Large Language Models (LLMs) and autonomous agents, it was clear that the browser needed a fundamental rethinking.
This insight sparked the creation of what would become our core offering: a platform that makes accessing cloud-based browser infrastructure as simple as an API call.
Much like self-driving cars were built to navigate roads originally designed for humans, Browserbase serves as the adapter that enables automated agents to seamlessly navigate the internet. We provide dedicated browsing infrastructure for your agents and automations, an approach that fundamentally differs from consumer-oriented browsers. Our browsers do not live on your device and do not collect your data. Browserbase runs in secure, isolated execution environments where customer data is never shared, sold, or used as training material for third-party AI models.
Browserbase enables developers to effortlessly launch tens, hundreds, or even thousands of browsers simultaneously. Traditionally, managing such infrastructure has been notoriously complex, fragile, and expensive. Without these obstacles, developers can concentrate on core business logic instead of browser configuration and maintenance.
Spinning up a browser is as easy as:
const bb = new Browserbase({ apiKey: process.env.BROWSERBASE_API_KEY }); const session = await bb.sessions.create({ projectId: process.env.BROWSERBASE_PROJECT_ID });
We, however, recognized that providing robust, trustworthy infrastructure was not enough. Developers also needed intuitive ways for agents to interact seamlessly with the web. Existing frameworks were brittle, hard to use, and often required deep expertise to maintain. These technical hurdles served as fundamental barriers to the broader adoption of web automation. Enter Stagehand.
Stagehand bridges the gap between precise, step-by-step web automations and fully autonomous browsing agents. On one end of the spectrum, carefully scripted automations offer granular control, high-speed execution, and avoid costly inference steps. On the other end, fully autonomous agents are flexible, resilient to website changes, and continuously improve as the underlying models advance.
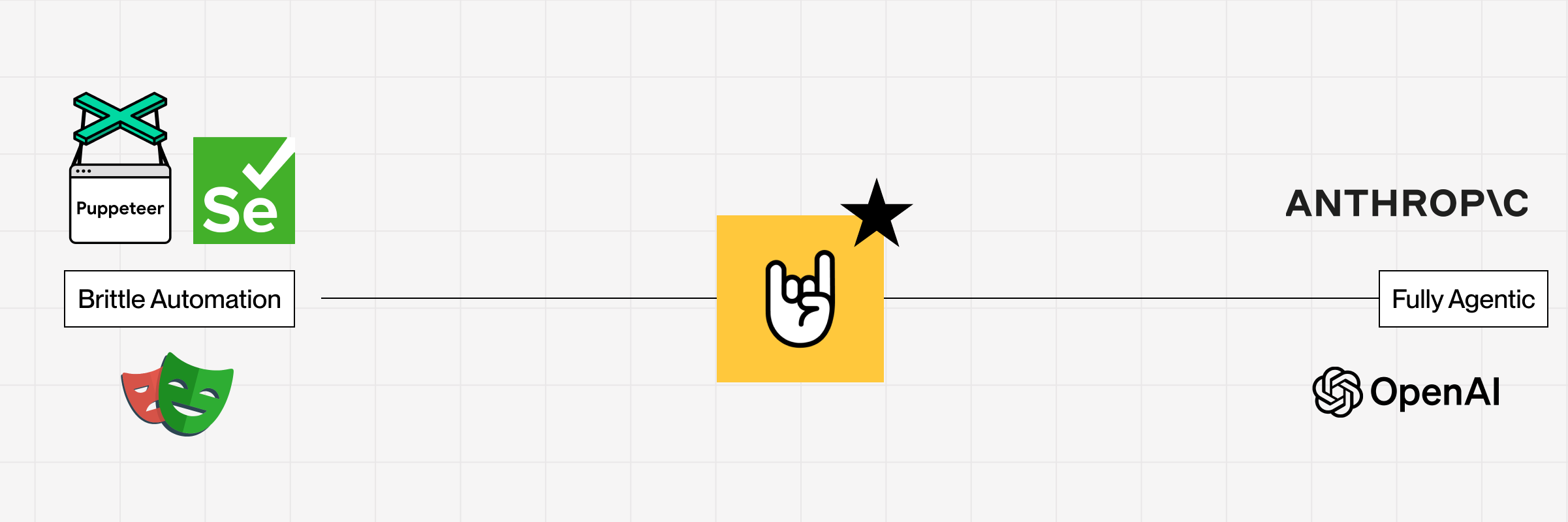
Stagehand balances these approaches by allowing users to define individual web interactions in natural language. Users specify actions like "click the login button" or "type my email address," and Stagehand translates these into actionable browser steps. By decomposing complex automations into natural language steps, Stagehand ensures that each AI-enabled action remains focused on a single, unambiguous objective, improving model reliability and accuracy.
Stagehand also minimizes inference costs through its action caching mechanism. As it executes your commands, Stagehand identifies page elements and caches them for future runs, making automation faster and cheaper over time. When websites change, the framework gracefully falls back to AI and rebuilds its cache without disrupting your automation.
Beyond navigation, Stagehand provides a simple interface to extract structured data from any webpage. You define the desired schema, and it intelligently pulls the information you need, whether it's product details, pricing tables, or complex nested data.
The result is a complete automation system that transforms web interaction and data extraction into plain English instructions that are self-documenting, instantly understandable by any team member, and resilient to the constant evolution of the web. You write what you want to happen, Stagehand figures out how to do it, and then remembers the solution for next time. Here's what this looks like in practice:
// Step 1: Navigate to URL await page.goto('https://www.nasdaq.com/'); // Step 2: Perform action await page.act('click the earnings link'); // Step 3: Extract data const extractedData = await page.extract({ instruction: 'extract all companies announcing earnings this week with their symbol, company name, market cap, fiscal quarter ending, consensus EPS forecast, and timing (pre-market or after-hours)', schema: z.object({ companies: z .array( z.object({ symbol: z.string().optional(), companyName: z.string().optional(), marketCap: z.string().optional(), fiscalQuarterEnding: z.string().optional(), consensusEPSForecast: z.string().optional(), timing: z.string().optional(), }), ) .optional(), }), });
The combination of Browserbase and Stagehand dramatically reduces the friction for developers creating automations or providing web access to their agents. Yet despite these advances, a significant technical barrier remained. The legacy applications and workflows that desperately need automation are often managed by professionals focused on their domain expertise: doctors managing patient systems, accountants navigating financial platforms, and operations teams coordinating across multiple platforms.
This gap became crystal clear when we started receiving calls from non-technical builders trying to implement Browserbase and Stagehand automations but struggling to translate their workflows into code. These conversations sparked an insight: what if you could directly harness the full power of browser automation without writing a single line of code?
Enter Director. Director takes the powerful foundation of Browserbase and Stagehand and makes it accessible to everyone. Users describe their high-level tasks, such as "download all invoices from last month" or "update inventory across these three platforms," and Director autonomously generates and executes the necessary Stagehand code. Throughout execution, Director leverages Browserbase to perform the task in real-time, self-correct when encountering obstacles, and adapt its approach until the task is complete. It unlocks web automation for the millions of people who know exactly what they need to automate; and they shouldn’t have to learn to program to make it happen.
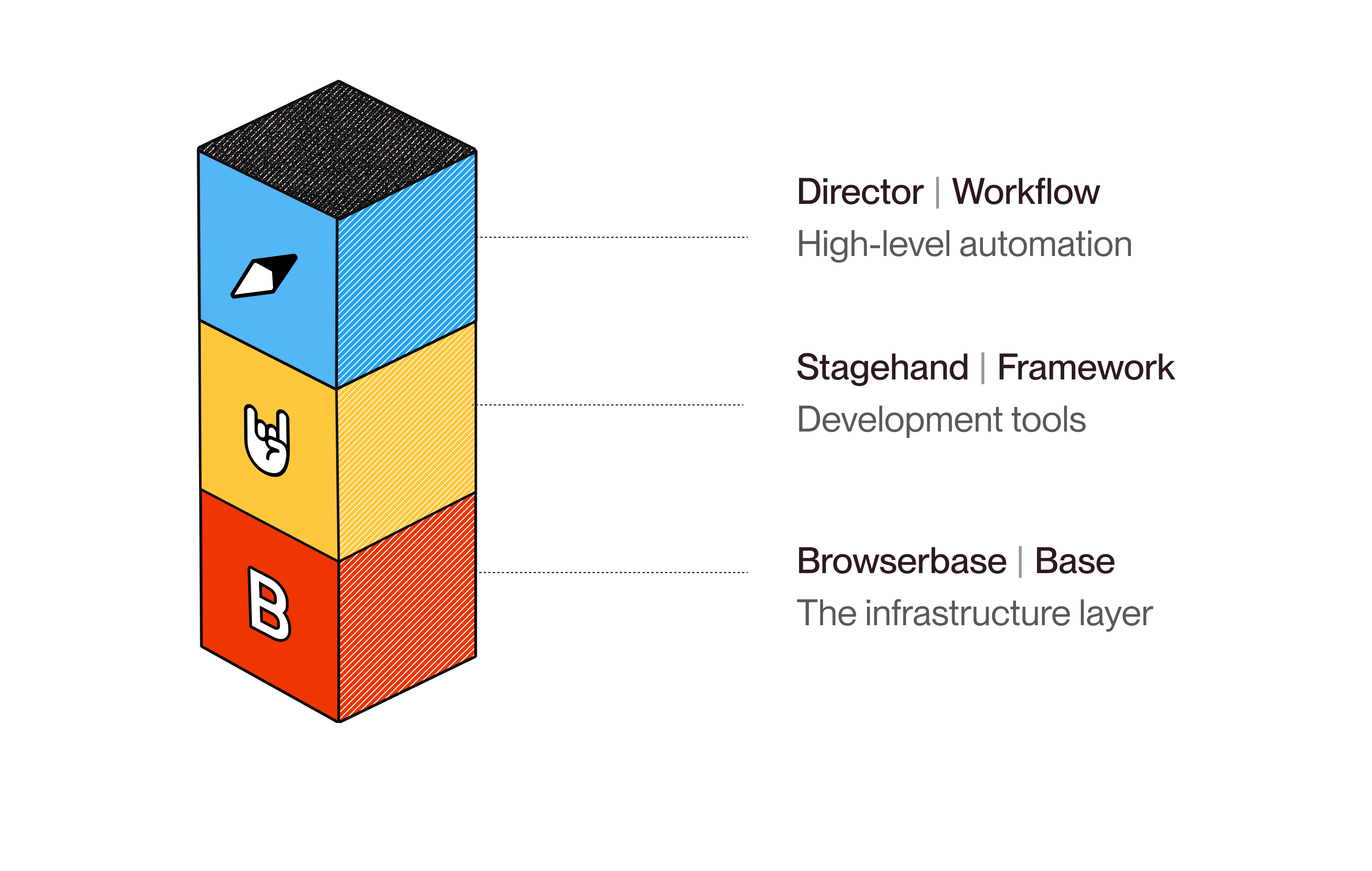
This completes the vision: Browserbase provides the infrastructure, Stagehand offers the intelligent automation layer, and Director makes it all accessible to anyone who can describe their problem. The technical complexity remains under the hood, but the user experience becomes as simple as having a conversation. The result, however, is not just another developer tool or automation framework. It's a push towards a fundamental shift in how humans interact with the digital systems that increasingly dominate our working lives.
Every day, millions of professionals waste countless hours on operational overhead. When we free professionals from clicking through the same workflows day after day, we create space for creativity, strategic thinking, and the uniquely human work that actually matters. The boring work dies so that the interesting work can flourish.
The internet was built for human consumption, but it’s increasingly navigated by agents on our behalf. Browserbase ensures those agents have the tailored, trusted infrastructure they need. Stagehand gives them the tools to navigate complexity. Director extends that power to everyone, regardless of technical expertise. Together, they form a complete ecosystem for web automation that scales from simple tasks to complex workflows, from individuals to enterprise systems.
We are building a future where Browserbase will be remembered for unlocking capabilities that AI alone could not reach. A future where the friction between human intent and digital execution disappears entirely. Where describing what you want is enough to make it happen, and the only limit to automation is your ability to imagine what's possible.
If you’re interested in building the future of web automation with us, we’re hiring.